[TOC]
Map特性
键值对
不继承Collection
键唯一
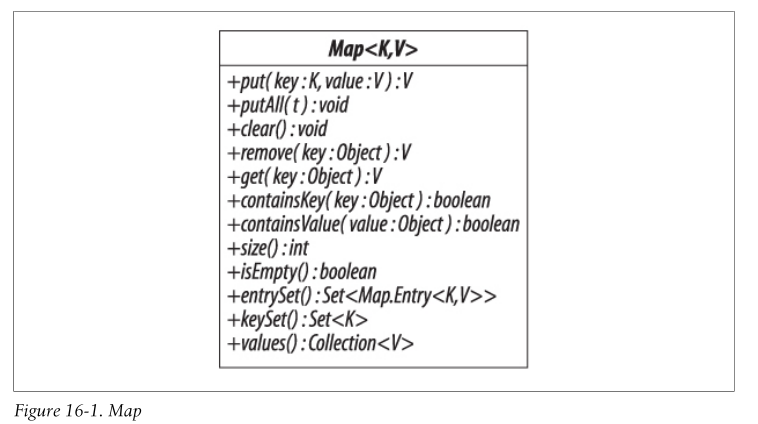
Map方法
添加联系
1 | V put(K key, V value) // add or replace a key-value association |
移除联系
1 | void clear() // remove all associations from this map |
查询Map内容
1 | V get(Object k) // return the value corresponding to k, or |
修改(1.8添加)
1 | default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> |
提供keys、Values、Associations视图
1 | Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() // return a Set view of the associations |
视图与原集合是有关联的
ps:清空HashMap O(n)时间复杂度
clients.removeAll(Collections.singleton(acme));
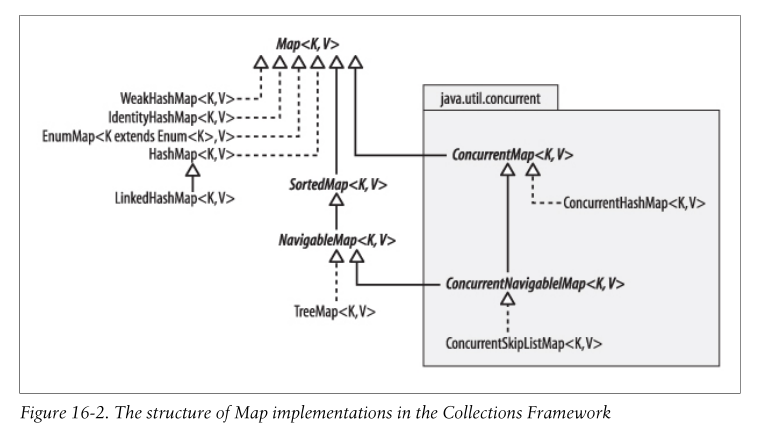
Map的实现
HashMap
hashmap构造
1 | public HashMap(int initialCapacity) |
容量确定
默认16
HashMap的bucket 数组大小一定是2的幂,若不是,寻找最近的的2的幂
该算法让最高位的1后面的位全变为1
1 | //|=:n与后面的数做或运算 |
loadFactor加载因子
默认0.75f
loadFactor加载因子是控制数组存放数据的疏密程度(01,稀疏密集)
冲突数<6转链表,>=8转红黑树(因为泊松分布)
put过程
put过程:(1.8)
1、 如果定位到的数组位置没有元素 就直接插入。
2、如果定位到的数组位置有元素就和要插入的key比较,如果key相同就直接覆盖,如果key不相同,就判断p是否是一个树节点,如果是就调用e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value)将元素添加进入。如果不是就遍历链表插入(插入的是链表尾部)。
put过程:(1.7)
1、如果定位到的数组位置没有元素 就直接插入。
2、如果定位到的数组位置有元素,遍历以这个元素为头结点的链表,依次和插入的key比较,如果key相同就直接覆盖,不同就采用头插法插入元素。
resize过程
resize
1.7:
初始化一个大小为(capacity x 2)的新数组,将原数组在hash至新数组中。
链表元素会倒置
1.8:
桶中存在一个链表,需要将链表重新整理到新表当中,因为((newCap = oldCap << 1)所以原节点的索引值要么和原来一样,要么就是原(索引+oldCap)和JDK 1.7中实现不同这里不存在rehash
迭代器
迭代器快速失效
LinkedHashMap
构造
1 | public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, |
Hashmap实体中添加before,after(双向链表)实现有序访问
LinkedHashMap添加head、tail(头指针和尾指针)
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest)
accessOrder
accessOrder: 为 false按插入顺序访问;为true,按访问顺序访问(LRU算法)
LRU实现
1 | protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) |
可以重载该方法自己定义策略
是否线程安全
不安全,迭代器快速失效
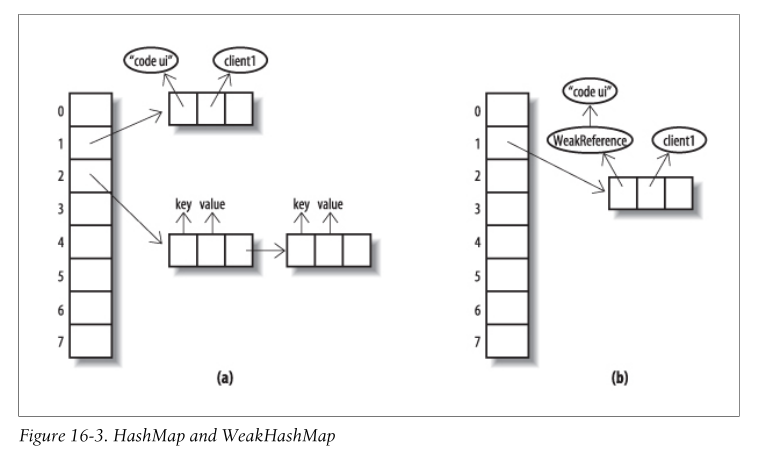
WeakHashMap
用途
回收原理
gc判断是否为弱引用(有没被其他代码使用)若是回收key,将value放入referencequeue;
weakhashmap会在下一次调用expungeStaleEntries方法时回收value;
是否线程安全
不安全,迭代器快速失效
IdentityHashMap
用途
序列化
深度复制
记录对象代理
记录jvm对象
构造函数
1 | public IdentityHashMap() |
默认大小32
默认加载因子为0.67
1 | private static int capacity(int expectedMaxSize) { |
初始化一个数组(大小为给定值转为最接近2的幂的值且大于等于给定数 * 2)
处理hash冲突
使用线性探针法,如下图: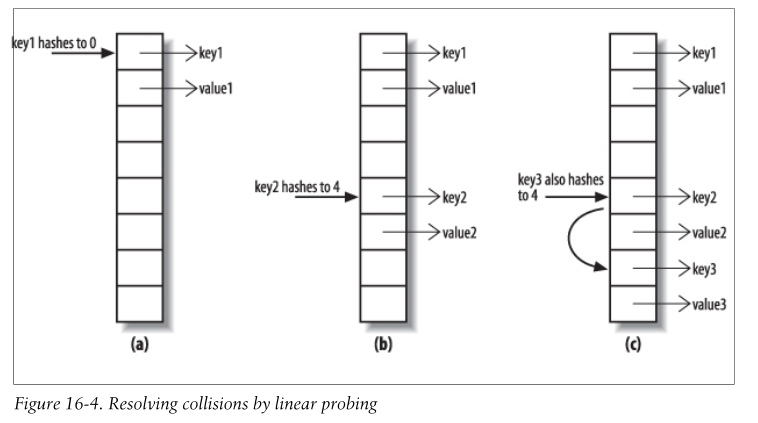
判定相等
与hashmap不同
identityhashmap是判断key1和key2的地址是否相等的(key1==key2)
扩容
元素达到阈值时,会进行扩容处理,扩容后会旧表中的元素重新hash到新表中
删除元素
在删除一个元素后会进行一次closeDeletion处理,重新分配元素的位置
EnumMap
EnumMap代替叙述索引
key不能为null,value可以
SortedMap和NavigableMap
SortedMap接口
sortedmap接口已经被navigablemap接口替代(与sortedset和mavigableset类似)
获取第一个元素和最后一个元素
1 | K firstKey() |
若无元素,返回 NoSuchElementException
获取比较器
1 | Comparator<? super K> comparator() |
查看子元素
1 | SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) |
NavigableMap接口

获取第一个元素和最后一个元素
1 | Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() |
获取范围视图
1 | NavigableMap<K,V> subMap( |
可以选择是否包括上界和下界
获取最近比配的数据
1 | Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K Key) |
Navigating the Map
1 | NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() // return a reverse-order view of the map |
TreeMap
构造
除了空构造和通过map构造,treemap还提供了一下两种构造函数
1 | public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) |
其他特性
get ,put和 remove操作花费O(log n) 时间复杂度
迭代器快速失效
ConcurrentMap接口
为高并发场景下的Map提供原子操作
1 | V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) |
ConcurrentHashMap
实现原理
1.7
采用乐观读+分段锁实现 来 实现ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentHashMap 是由 Segment 数组结构和 HashEntry 数组结构组成
Segment 实现了 ReentrantLock
1.8
采用CAS和synchronized来保证并发安全。数据结构跟HashMap1.8的结构类似,数组+链表/红黑二叉树。synchronized只锁定当前链表或红黑二叉树的首节点,这样只要hash不冲突,就不会产生并发,效率又提升N倍
其他
默认容量16
在获取size()会导致全锁,开销大
构造函数提供并发级别控制
1 | ConcurrentHashMap() |
ConcurrentNavigableMap
ConcurrentSkipListMap
是concurrentskiplistset的底层实现get , put , and remove 花费O(log n) 时间
迭代器快速失效
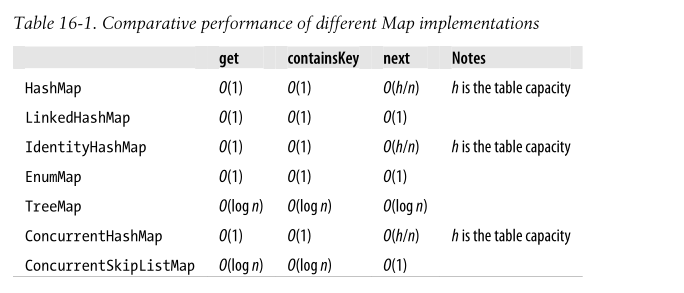
Map实现的对比